A facile, robust and scalable method for the synthesis of Pd nanoplates with hydroxylamine as a reducing agent and mechanistic insights from kinetic analysis†
Abstract
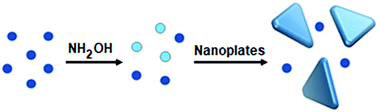
Nanocrystals lined with stacking faults have received much attention in recent years due to their typical anisotropic, plate-like geometry and their perplexing formation mechanism. In this report, we introduce a simple and reliable method for the scalable production of Pd nanoplates containing stacking faults. The success of our protocol was reliant on the use of hydroxylamine as a reducing agent, which allowed the nucleation and growth of well-defined Pd nanoplates with an average edge length of 24.5 ± 6.6 nm and a thickness of 4.7 ± 0.4 nm. We conducted a kinetic analysis to validate the importance of an appropriate initial reduction rate in determining the formation of seeds lined with stacking faults. To demonstrate the robustness of this synthesis, we conducted a set of control experiments under different experimental conditions such as acidity, temperature, and chemical environment and demonstrated that Pd nanoplates could be obtained as final products in all scenarios. We further extended the batch-based synthesis to a continuous flow reactor, moving one step closer towards high-volume production. Taken together, this method offers both simplicity and reproducibility for the synthesis of Pd nanoplates, which will enable future mechanistic studies and applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...