Enhanced performance and mechanical durability of a flexible solar cell from the dry transfer of PEDOT:PSS with polymer nanoparticles†
Abstract
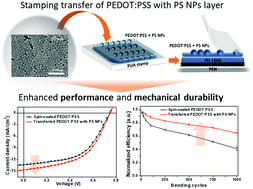
Stamping transfer has been considered as an alternative process for fabricating organic photovoltaic devices because of its various advantages such as a simple, flexible, and repeatable process, which is suitable for large-area fabrication. In this study, we fabricated organic flexible solar cells with enhanced cell performance and mechanical durability by performing a simple dry transfer of a poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) hole transport layer (HTL) with polystyrene nanoparticles (PS NPs). In order to ensure the stable flexibility of these flexible solar cells, cross-linked PS NPs synthesized with a size of 70 nm were introduced to the PEDOT:PSS HTL. The transfer of the PEDOT:PSS layer with PS NPs onto the polymer electrode (PH1000) was performed completely via stamping transfer with a polyurethane acrylate stamp. The power conversion efficiency of the PTB7:PC71BM-based flexible devices prepared by the transfer of PEDOT:PSS with PS NPs was 5.71%, which was higher than that of the spin-cast device without PS NPs (5.37%). The tuned morphology of the PEDOT:PSS achieved through transfer and the increased surface area of the PEDOT:PSS resulting from the corrugated structure provided by the protruding PS NPs improved the charge transport from the active layer to the PEDOT:PSS HTL. This in turn resulted in an enhanced short-circuit current density. In addition, the introduced PS NPs significantly improved the mechanical stability of these flexible devices, allowing the devices prepared by the transfer of PEDOT:PSS with PS NPs to tolerate more cycles of strain in the bending test. The introduced PS NPs enhanced the mechanical strength of PEDOT:PSS by acting as not only binders within PEDOT:PSS, but also as interfacial modifiers which can improve the interfacial adhesion between the active layer and PEDOT:PSS HTL. Thus, the transfer of a PEDOT:PSS layer with PS NPs will contribute to the long-term operation of flexible solar devices with enhanced device performance and mechanical durability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...