Site-selective growth of Ag nanocubes for sharpening their corners and edges, followed by elongation into nanobars through symmetry reduction†
Abstract
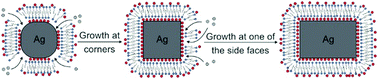
It remains a challenge to synthesize Ag nanocubes with sharp corners and edges while retaining a compact size below 20 nm. Here we demonstrate the use of site-selective growth to sharpen the corners and edges of truncated Ag nanocubes with sizes down to 18 nm, followed by their elongation into nanobars with aspect ratios up to 2. The key to the success of this synthesis is the site-selective deposition at corners and edges, as enabled by cetyltrimethylammonium chloride (CTAC). While CTA+ is an effective colloidal stabilizer, Cl− can react with Ag+ to generate AgCl precipitates, slowing down the reduction kinetics. In addition, Cl− can serve as a facet-selective capping agent towards the {100} side faces and thereby confine the growth mainly to corners and edges. Interestingly, once all the corners and edges have been sharpened, the growth is switched to an asymmetric mode to favor deposition on one of the six side faces only, leading to the formation of Ag nanobars with controllable aspect ratios. The symmetry reduction takes place as a result of the limited supply of Ag atoms, the strong capping of Cl− ions towards the {100} facets, and the possible involvement of localized oxidative etching caused by Cl−/O2. We also demonstrate that the Ag nanocubes with sharp corners and edges can serve as a better sacrificial template than their truncated counterparts in generating Au hollow nanostructures with ultrathin walls.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...