Simultaneous tuning of martensitic transformation behavior, magnetic and mechanical properties in Ni–Mn–Sn magnetic alloy by Cu doping
Abstract
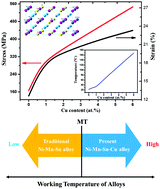
As typical multiferroic materials with a large magnetoelastic effect, which is based on giant caloric effects, Ni–Mn–Sn ferromagnetic shape memory alloys are regarded as potential environmentally friendly solid-state refrigeration materials. The significant brittleness of these alloys and their low martensitic transformation temperatures limit their practical applications. We propose a new means of performance tuning, which shows that replacing Sn by Cu in Ni47Mn38Sn15−xCux magnetic shape memory alloys can simultaneously tune their martensitic transformation behavior and magnetic and mechanical properties. When 6 at% Cu is added, a maximum compressive strength of 546 MPa with a fracture strain of up to 23.4% can be achieved at room temperature. The substitution of Cu for Sn also markedly increases the martensitic transformation temperature from 22.2 °C to 167.9 °C, which is crucial for actual applications. Moreover, using first-principles calculations, we clarify the effect of the substitution of Cu for Sn on the martensitic transformation behavior. On the basis of the above idea, we anticipated that a high-temperature magnetic shape memory alloy with excellent mechanical properties would be obtained by doping with Cu and another element simultaneously. This design method will solve a bottleneck in the development of high-temperature magnetic memory alloys.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...