Sequential delivery of bismuth nanoparticles and doxorubicin by injectable macroporous hydrogels for combined anticancer kilovoltage X-ray radio- and chemo-therapy†
Abstract
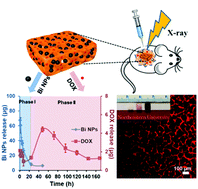
Sequential delivery systems are required to maximize synergistic anticancer therapeutic effects in combined X-ray radio- and chemo-therapy. Here, we described an injectable macroporous hydrogel as a sequential delivery platform for combined kilovoltage X-ray radio- and chemo-therapy of 4T1 breast cancer. The macroporous hydrogel offered two sequentially distinct delivery profiles for co-loaded radiosensitizers (bismuth nanoparticles, Bi NPs) and an anticancer drug (doxorubicin, DOX). Bi NPs were released preferentially and completely over 24 h; however, DOX was released slowly in the first 24 h and was sustainedly released over one week. This sequential release behavior of Bi NPs and DOX in macroporous hydrogels achieved significantly synergistic antitumor effects in vitro. In vivo studies further indicated that this macroporous hydrogel in interaction with kilovoltage X-ray radiation could effectively inhibit tumor growth and dramatically improve the survival ratio in mice to 100%. Furthermore, the released Bi NPs from macroporous hydrogels could be dissolved and discharged from the body as soluble bismuth ions after treatment. These results suggested that the injectable macroporous hydrogel may serve as a combinational therapeutic platform for clinical superficial cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...