Endothelial mimetic multifunctional surfaces fabricated via polydopamine mediated copper immobilization
Abstract
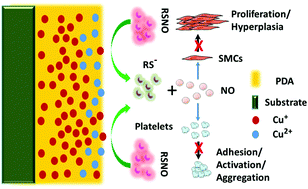
Nitric oxide (NO), which is continuously released from the normal healthy endodermis cell layer of the vascular system, plays a crucial role in the stability and health maintenance of blood vessels. It is one of the most important gaseous signaling molecules and regulates cardiovascular homeostasis, inhibits blood clotting and intimal hyperplasia, and prevents atherosclerosis. Insufficient NO production is often observed in atherosclerosis lesions. In this work, a NO-generating bioactive coating built by a polydopamine film (PDA) and a copper ion was fabricated. The coating (Cu/PDA) had glutathione peroxidase (GPx)-like activity and was able to catalyze NO release from S-nitrosothiols (RSNOs) due to the catalytic activity of the copper ion. It was also capable of catalyzing RSNO decomposition and NO production. The copper ion was embedded in the PDA coating to ensure the effectiveness of long-term NO-catalytic activity. The surface exhibited a favorable suppression of vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation and also efficiently reduced thrombosis formation. Additionally, the NO catalytic surface had a positive influence on endothelial cell (EC) growth behavior. The in vivo study verified that the modified surface promoted healthy endothelium formation and suppressed intimal hyperplasia, which is conducive to re-endothelialization and for reducing restenosis of vascular stents. This work provides a potential strategy for the development of novel cardiovascular implants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...