Mammalian cells: a unique scaffold for in situ biosynthesis of metallic nanomaterials and biomedical applications
Abstract
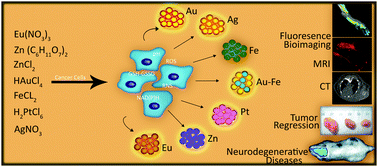
Production of nanoscale materials often requires the use of toxic chemicals and complex synthetic procedures. A new scaffold has been explored for in situ synthesis of nanomaterials that utilizes natural biological systems in the form of plants, bacteria, fungi, algae and redox-imbalanced mammalian cells and systems. The latter approach has become popular in recent years and has shown some promising results in bioimaging of cancer, as well as inflammatory and neurodegenerative maladies. Biosynthesis of nanoclusters in redox-imbalanced mammalian cells is facile, cost-effective and environmentally friendly with higher biocompatibility and target specificity and lower adverse effects than traditional synthetic approaches. Herein, we describe recent advances in mammalian green in situ biosynthesis for biomedical applications, especially in cancer and neurodegenerative disease theranostics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...