Reduced graphene oxide nanoribbon immobilized gold nanoparticle based electrochemical DNA biosensor for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis†
Abstract
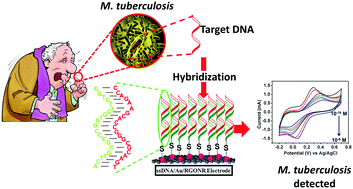
Tuberculosis is one of the most dreadful diseases caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis with more than 9 million individuals suffering from it in 2014. Traditional methods of detection are not efficient enough for its quick and reliable detection; therefore, it is imperative to develop methods of its detection in the early stages. Consequently, we report a highly sensitive and selective biosensor for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In this work, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs, dia. ∼6 nm, 1.81 wt% loading) are immobilized over reduced graphene oxide nanoribbons (RGONRs). An ssDNA/Au/RGONR electrode is prepared by immobilizing Au nanoparticles followed by covalent modification of Au nanoparticles with 5′SH-ssDNA. As per the best knowledge of the authors, the target DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is detected using a ssDNA/Au/RGONR bioelectrode by cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometric methods for the first time. With high detection efficiency (0.1 fM), the ssDNA/Au/RGONR bioelectrode exhibited better signal amplification and electrochemical response as compared to bare Au and RGONR electrodes. Additionally, the ssDNA/Au/RGONR bioelectrode displayed good linear response to different concentrations of target M. tuberculosis DNA. The ssDNA/Au/RGONR has shown excellent specificity (92%) to Mycobacterium tuberculosis target DNA as compared with non-complementary DNA. The Au/RGONR matrix has the potential to be used as an immobilization platform for single-stranded probe DNAs of different diseases other than tuberculosis reported here.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...