Phenanthriplatin(iv) conjugated multifunctional up-converting nanoparticles for drug delivery and biomedical imaging†
Abstract
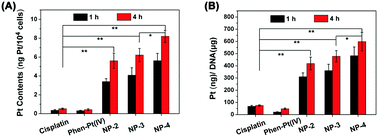
Platinum-based drugs cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin are widely used in the clinical treatment of cancer. However, the clinical applications of platinum-based drugs are greatly limited by the side-effects, lack of selectivity, fast blood clearance, and intrinsic or acquired drug resistance. In this study, we report an anticancer drug delivery system based on phenanthriplatin(IV) (Phen-Pt(IV))-conjugated NaGdF4:Yb3+/Er3+ nanoparticles. The upconversion luminescent NaGdF4:Yb3+/Er3+ nanoparticles (UCNPs) were further modified with polyethyleneimine (PEI), poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and the cancer targeting ligand arginine–glycine–aspartic peptide (RGD), resulting in the formation of water-dispersible and biologically functionalized UCNP@PEI–Phen-Pt–PEG–RGD nanoparticles. The Phen-Pt-conjugated UCNP@PEI–Phen-Pt–PEG–RGD nanoparticles exhibited an obvious cytotoxic effect on Hep-2 cells (Human Laryngeal Carcinoma cell line) via MTT assay. Meanwhile, the endocytosis process of Phen-Pt-conjugated NaGdF4:Yb3+/Er3+ nanoparticles by Hep-2 cells was demonstrated through flow cytometry and ICP-MS. In addition, the upconversion luminescence image of UCNP@PEI–Phen-Pt–PEG–RGD taken up by cells shows green emission under 980 nm infrared laser excitation, making the UCNP@PEI–Phen-Pt–PEG–RGD nanocomposites promising candidates as bioimaging agents. Moreover, these UCNPs were further explored for in vitro and in vivo T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. The in vivo experiments on mice also confirmed that the Phen-Pt(IV)-conjugated nanoparticles have a relatively high tumor inhibition rate. These results indicate that the multifunctional nanoparticles can be expected to be a platform for simultaneous imaging and cancer therapeutic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...