Covalently functionalized amide cross-linked hydrogels from primary amines and polyethylene glycol acyltrifluoroborates (PEG-KATs)†
Abstract
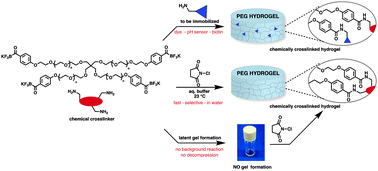
A new method for the rapid preparation of chemically cross-linked hydrogels based on a multi-arm polyethylene glycol (PEG) bearing potassium acyl trifluoroborate (KAT) functional groups with multi-dentate amines is described. These scaffolds – prepared in aqueous buffer – give strong, transparent hydrogels. At pH 3, the gel formation is complete within seconds, and the reaction rate can be tuned by modulating the pH. Rheology measurements show that the hydrogel properties can be tuned as a function of both the weight percent of solids in the gel and the denticity of amine cross-linker, allowing for predictable formation of gels with desired traits. This process relies on a rapid amide-forming reaction of KATs and in situ generated N-chloroamines. Numerous commercially available amines, including di-, tri- and tetra-functional amines as well as peptides and carbohydrates serve as effective cross-linkers. Monodentate amines included in the gelation mixture are covalently linked into the gel matrix by amide-bonds, allowing gels containing immobilized molecules including dyes, sensors, or biotin amine, to be prepared in a single step from simple starting materials. The ability to induce gelation only upon addition of equimolar amounts of an inexpensive inducer (N-chlorosuccinimide) allows premixed components to be stored as an aqueous solution for weeks and converted to gels on demand.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...