Sustained antibacterial activity of berberine hydrochloride loaded supramolecular organoclay networks with hydrogen-bonding junctions†
Abstract
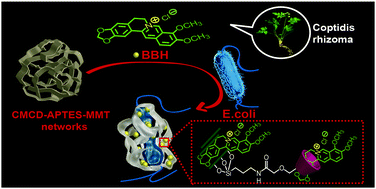
The environmental risk from antibiotics is an issue of increasing concern. So, carboxymethyl β-cyclodextrin-functionalized montmorillonite nanosheets were for the first time successfully synthesized through a cheap, environmentally friendly and scalable approach and confirmed by FTIR, XRD and TGA. FE-SEM investigation showed that the resulting functional material could be further self-assembled into dense supramolecular organoclay networks (D-networks). The antibacterial properties of the D-networks loaded with natural berberine hydrochloride (BBH) were investigated toward E. coli and S. aureus by using colony growth on agar plates, bacterial growth curves based on optical densities, and confocal and fluorescence microscopy. Our studies demonstrated that the BBH loaded D-network antibacterial activity was concentration dependent and significantly exceeded that of free BBH. FE-SEM observation confirmed that E. coli and S. aureus can directly contact the D-networks and confocal and fluorescence microscopy showed that free BBH was only very poorly internalized, while the BBH released from the BBH-loaded D-network could be internalized efficiently into bacterial cells, resulting in an increment of the intracellular BBH level compared with the free BBH group. Time-dependent antibacterial activity was observed and it was found that the BBH-loaded D-network dispersion at the BBH dosage of 600 μg mL−1 almost completely suppressed the growth of E. coli, leading to a viability loss of up to 98.45 ± 1.22%, while the BBH-loaded D-network dispersion at the BBH concentration of 250 μg mL−1 exhibited a growth inhibition of 97.81 ± 0.83% toward S. aureus over three days. Our results suggest that supramolecular organoclay networks, in the future, may function as promising antibacterial drug carrier systems to promote BBH delivery in E. coli and S. aureus, which can reduce the environmental risk of antibiotics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...