All-in-one hyperbranched polypeptides for surgical adhesives and interventional embolization of tumors†
Abstract
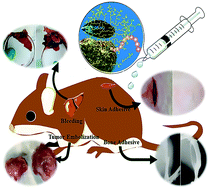
A series of hyperbranched, thermo-responsive and mussel-inspired polypeptides were synthesized and used for surgical adhesion, hemostasis and interventional embolization. These polypeptides showed excellent tissue-adhesive properties according to adhesive strength tests on porcine skin and bone in vitro, where the maximum lap-shear adhesion strength on porcine skin was 114.5 kPa and the maximum tensile adhesion strength on bone was 786 kPa. In vivo animal experiments indicated that these polypeptides exhibit superior hemostatic properties and healing effects in skin incisions and osteotomy gap; the skin incision healing and osteotomy gap remodeling were completed in all rats after 14 and 60 days, respectively. In vivo evaluation of the embolization ability of these polypeptides was performed on rabbit kidney models, resulting in successful occlusion of renal arteries, which led to gross ischemic changes in the embolized kidneys up to 16 days. A trial embolization procedure on H22 tumor-bearing rat models also confirmed the gelability of these polypeptides in tumor arteries, which might cause damage to embolized tumors. Therefore, these polypeptides are expected to be good candidates as surgical tissue adhesives, antibleeding materials, and effective embolic materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...