Controlled grafted poly(quaternized-4-vinylpyridine-co-acrylic acid) brushes attract bacteria for effective antimicrobial surfaces†
Abstract
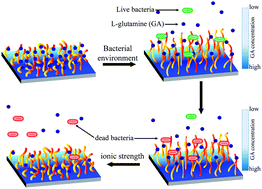
Copolymer poly(quaternized-4-vinylpyridine-co-acrylic acid) (P(Q4VP-co-AA)) brushes with an adsorbed amino acid (L-glutamine (GA)) were grafted onto surfaces as a means of attracting, contact-killing, and releasing bacteria. The substrates, silicon wafer (SW), glass, and PDMS, were coated with 7-octenyltrichlorosilane (7OTS), and this was followed by surface-initiated reversible addition–fragmentation transfer (SI-RAFT) polymerization. The 7OTS allowed easy control of the grafting density, and a maximum grafting density of 0.36 chains per nm2 was obtained. The GA was initially adsorbed to the P(Q4VP-co-AA) brushes, and ultimately desorbed in a microbial environment-created concentration gradient, causing microbial movement toward the decorated surfaces. The P(Q4VP-co-AA) brushes at SW, glass, and PDMS substrates enabled the contact-killing of 90 ± 4, 93 ± 5, and 92 ± 3% of Escherichia coli and 92 ± 4, 93 ± 3, and 91 ± 4% of Staphylococcus aureus, respectively, from microbial concentrations of 1 × 105 CFU mL−1 and 30 min exposures. After contact-killing, these brushes completely released the microbes when they were dipped in NaCl (1 M) solution for 5 min. The ease of controlling the grafting density and substrate modification as well as the microbial attraction capability, high contact-killing efficiency, and self-sterilizing make P(Q4VP-co-AA)–GA brushes a useful material for the development of multi-functional antimicrobial substrates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...