Computer-aided design of short peptide ligands targeting tumor necrosis factor-alpha for adsorbent applications†
Abstract
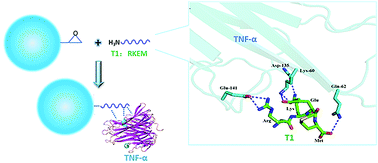
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine active in the bodily immune response and serious inflammatory diseases. Traditional ligands targeting TNF-α focus on antibodies and receptors, which always associate with low efficacy and specificity. In the present study, two peptide ligands (T1: Ac-RKEM-NH2 and T2: Ac-RHCLS-NH2) were designed by computer simulation technology considering the weak interactions between TNF-α and its receptor TNFR1. Calculations of binding free energy (BFE) were made by the Molecular Mechanics Poisson–Boltzmann Surface Area (MM-PBSA) method between T1 or T2 and TNF-α (−22.68 and −14.23 kcal mol−1, respectively). To assess the affinity levels, short peptide ligands were fixed on polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) microspheres; adsorption tests showed a stronger affinity of both PVA-T1 and PVA-T2 to TNF-α in PBS buffer than PVA microspheres (79.20 ± 1.32 and 74.27 ± 1.10 vs. 39.03 ± 1.25 pg mg−1, respectively). Moreover, PVA-T1 (74.8%, 17.60 ± 2.98 pg mg−1) and PVA-T2 (63.2%, 15.30 ± 4.81 pg mg−1) exhibit significantly enhanced TNF-α adsorption from the plasma of rats with sepsis to blank PVA and commercial XAD-7 resin. In conclusion, our results show that T1 designed by computer-aided molecular design (CAMD) exhibits a stronger affinity to TNF-α and it can significantly enhance PVA microsphere adsorption efficiency of TNF-α in plasma.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...