Fabrication of inherently radiopaque BaSO4@BaAlg microspheres by a one-step electrospraying method for embolization†
Abstract
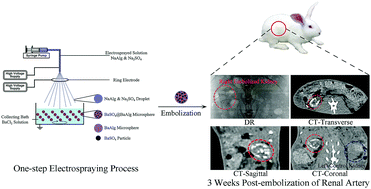
A new one-step electrospraying method is developed to fabricate intrinsic X-ray imaging barium alginate microspheres loaded with in situ synthesized BaSO4 particles (BaSO4@BaAlg microspheres). The electrospraying method is straightforward and environmentally friendly, involving only the aqueous phase without any extra surfactant. It is also flexible. By varying the parameters of electrospraying, monodispersed BaSO4@BaAlg microspheres with a diameter range from 200 to 1800 μm are achieved and meet the requirements for precisely calibrated embolics and flexible clinical applications. BaSO4@BaAlg microspheres possess long-term X-ray imaging capability, which shows their own location and distribution precisely in real time during transcatheter arterial embolization operations, and they can be used for noninvasive examinations after operations. The in vitro X-ray-visible stability test demonstrates that the X-ray imaging capability of the BaSO4@BaAlg microspheres is extremely stable. The fluctuation of radiodensity is within 7% of its original value over 52 days. Furthermore, the digital radiography and computed tomography images of a renal artery embolized with the BaSO4@BaAlg microspheres confirm that in vivo visibility under X-ray is kept constant for an embolization period of 3 weeks. Angiographic and histological studies on an embolized kidney verify that the microspheres completely occlude the blood vessels of the targeted kidney, including peripheral vessels.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...