A NIR rhodamine fluorescent chemodosimeter specific for glutathione: Knoevenagel condensation, detection of intracellular glutathione and living cell imaging†
Abstract
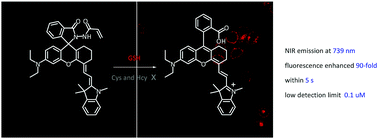
A new near-infrared probe for detecting glutathione based on conjugate addition and intramolecular amino induced spirolactam opening named RhAN was designed and synthesized. Firstly, rhodamine was reacted with 2-(1,3,3-trimethylindolin-2-ylidene) acetaldehyde by a Knoevenagel condensation, and the conjugate chain was extended, obtaining M2. Then, M2 was connected with hydrazide to get M3. Finally, the target molecule RhAN was synthesized via the combination of M3 and acryloyl chloride. In the presence of GSH, RhAN exhibits high selectivity, which specifically identifies GSH over Cys and Hcy, the color change from yellow to green together with the fluorescence appeared within 5 s, and there was no interference from the presence of other biological thiols and amino acids. The absorption and emission wavelength of the probe RhAN reached 717 nm and 739 nm, the molar extinction coefficient is 4.36 × 104 M−1 cm−1 and quantum yield is 0.26. Its absorption and emission intensity were enhanced by more than 117-fold and 90-fold upon addition of GSH, respectively. In addition, it also has high sensitivity with a low detection limit of 0.1 μM, which is lower than most previously reported GSH probes. The probe works excellently within a wide pH range of 2–10. Moreover, RhAN was employed for endogenous and exogenous imaging in MCF-7 cells for GSH. MCF-7 cells incubated with RhAN with GSH or blank RhAN all showed significant fluorescence in the red channel, which indicated that the probe could not only detect exogenous GSH, but it also permeated into the cells and reacted with the intracellular GSH. This is an excellent design for a fluorescence sensor, RhAN, as a quick and effective method for detecting excess GSH in living cells, for maintaining the balance of amino acids in the body and ensuring normal life activities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...