Construction of high surface potential polypyrrole nanorods with enhanced antibacterial properties†
Abstract
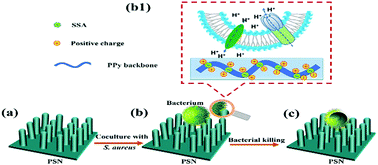
Conductive polymers (CPs) are frequently used as neural and osteogenic implants for signal recording and electrical stimulation due to their electroactive and good biocompatibility. However, these implants often fail due to bacterial infection. In this research, a novel nano-functionalized polypyrrole (PPy) with high surface potential was electrochemically developed to improve the antibacterial properties of CPs. Sulfosalicylic acid (SSA)—a biomolecule with abundant negatively charged functional groups—was introduced to not only successfully assist in the electrical assembly of Py micelles into a bacterial extracellular matrix mimetic nanostructure, but also to modulate the surface electrical properties of PPy. Scanning Kelvin probe microscopy (SKPM) results confirm the increased positive charges on SSA-assisted PPy (PPy/SSA nanorod and irregular PPy/SSA film) relative to the irregular PPy/Cl film. Plate colony-counting experiments confirm that SSA-assisted PPy has excellent antibacterial properties relative to the irregular PPy/Cl film. The higher antibacterial rate for PPy/SSA nanorods suggests a synergistic effect via the nanorod structure and the high surface potential induced by dopants. Cytotoxicity testing demonstrates that PPy/SSA samples were nontoxic to the cells. Our work provides an effective way to develop antibacterial CPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...