Heat shock protein-guided dual-mode CT/MR imaging of orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma tumor†
Abstract
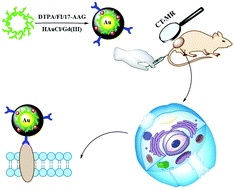
The development of an ultrasensitive nanoprobe is regarded as one of the most promising strategies for the precise diagnosis of tumors. Herein, tanespimycin (17-AAG)-modified polyethylenimine-based gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) co-labeled with a gadolinium (Gd) nanoprobe are constructed for targeted dual-mode computed tomography (CT)/magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. The specific binding of tanespimycin to the N-terminal of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) endows the modified nanoprobes (NPs) with the ability to up-regulate HSP90 tumor cells and to display excellent X-ray attenuation intensity and T1 MR imaging performance in an orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma tumor model. Such an ultrasensitive nanoprobe holds enormous promise for highly efficient tumor diagnosis and dual-mode CT/T1 positive MR imaging. This study develops a novel strategy to prepare a multifunctional nanoprobe via polyethylenimine nanotechnology. Using this strategy, various dual-mode or multimode nanoprobes for diagnosing different cancers may be designed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...