Bioinspired heptapeptides as functionalized mineralization inducers with enhanced hydroxyapatite affinity†
Abstract
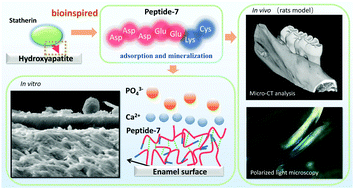
The regeneration of mineral crystals under physiological conditions is an efficient way to repair defects in hard tissues. To achieve robust mineralization on surfaces such as the tooth enamel, an inducer requires strong affinity with the substrates and should be able to induce mineralization. Thus far, most studies used a single molecule containing two components to realize the above functions separately, which might be troublesome to synthesize and purify. In this work, inspired by the statherin in the salivary acquired pellicle, we designed a simple peptide sequence, Asp–Asp–Asp–Glu–Glu–Lys–Cys (peptide-7), to accomplish the dual tasks of adsorption and mineralization on enamel surfaces. We speculate the calcium binding ability of the negatively charged carboxylic acid groups in the peptide itself contributes to the dual functions of peptide-7. In vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated its excellent repair effect on enamel as compared to fluoride. More importantly, due to the strong affinity between peptides and hydroxyapatite, a compact mineralized crystal layer and a strong adhesion between the regenerated minerals and the bottom substrates were observed, similar to the effect induced by fluoride. This work sheds light on the interaction mechanism between peptide-7 and minerals. In addition, since it is safer than fluoride, peptide-7 may have potential applications in the repair of other hard tissues and the functionalization of biomaterials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...