Extracellular retention of a cyclopamine nanoformulation leveraging larger size and more negative charge for improved breast cancer treatment†
Abstract
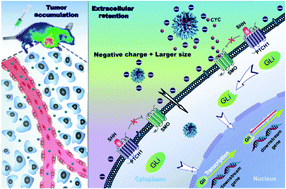
Compared with intracellular drug delivery, drugs with extracellular targeting sites are rarely considered. As one of these drugs, cyclopamine (CYC) is a promising anticancer drug that functions by targeting the cell membrane receptor. For improving therapeutic effect, an albumin-based nano-system (ABN) with the capacity for extracellular retention was developed. The ABN was formulated by incorporating bovine serum albumin (BSA) into nanoparticles at the denaturing temperature of BSA, with CYC acting as a hydrophobic nucleation site, followed by stabilization upon heat-induced disulfide cross-linking. The resultant ABNs are negatively charged with a nanoparticle size that can be delicately regulated by varying the reaction time. In MDA-MB-231 cells, the size and charge of ABNs significantly affected the extracellular retention capacity, with ABN-300 nm exhibiting an enhanced cytotoxic effect. In vivo fluorescence imaging revealed obvious and persistent tumor accumulation of ABNs. A therapeutic study in an orthotopic mammary fat pad tumor model shows that ABN-300 nm possesses the most remarkable antitumor effect compared with the control groups. These results provide a new strategy for improving the efficacy of drug targeting at extracellular sites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...