Superhydrophobic and slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces formed by the self-assembly of a hybrid ABC triblock copolymer and their antifouling performance†
Abstract
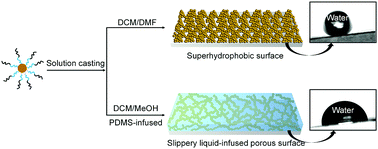
An ABC triblock copolymer based on poly(dimethylsiloxane)–poly(tert-butyl acrylate)–poly(methacrylolsobutyl POSS) is synthesized via combination of SET-LRP and ATRP from a PDMS macroinitiator. The resulting polymer can readily self-assemble into hierarchical structures through a stepwise “bottom-up” strategy, i.e. self-assembly followed by the nonsolvent vapor-induced phase separation. When a mixture of dichloromethane/dimethylformamide (DCM/DMF) is used as the casting solvent, the resulting surface (SHS) exhibits superhydrophobicity with a high water contact angle (156.7 ± 0.5°) and a low roll-off angle (<9°), and it also displays good self-cleaning property. Moreover, under the dichloromethane/methanol (DCM/MeOH) condition, a porous structure with intertwined networks of nano globules could be formed. Further infusion of the PDMS lubricant leads to the formation of a transparent slippery coating (SLIPS) with excellent water repellency, manifested by a low water contact angle hysteresis (∼3°) and a small sliding angle (∼6°). The SLIPS show excellent antifouling properties that effectively inhibit the attachment of P. aeruginosa ATCC 15692 as compared to that of the structured hydrophobic surfaces and cured PDMS surfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...