Tuning doping and surface functionalization of columnar oxide films for volatile organic compound sensing: experiments and theory†
Abstract
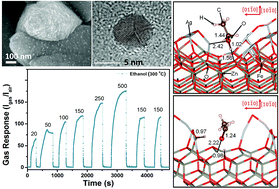
In this work, a new strategy based on the surface functionalization and doping of semiconducting oxides was proposed for tuning device properties. A considerable increase in the gas sensing ability of Fe-doped ZnO (ZnO:Fe) columnar films grown by chemical deposition is achieved via surface decoration with oxidized silver nanoparticles (AgO/Ag NPs) with a diameter of ∼7–10 nm. AgO/Ag-decorated ZnO:Fe (Ag/ZnO:Fe) samples showed an optimal operating temperature of 300 °C with fast recovery of the signal (∼7 s) and ultra-high sensitivity to ethanol vapor versus CH4 and H2 gases. The results presented demonstrate the potential for a significant increase in sensitivity to ethanol vapors by surface decoration with AgO/Ag NPs (density of ∼0.8 × 109 cm−2) while maintaining extremely high selectivity. Quantum mechanical simulations show that the transition metal oxide clusters modify the surface chemistry of the doped zinc oxide ZnO (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surface to improve ethanol sensing. Using thermodynamic arguments, we have investigated the substitutional Fe doping of the symmetrically different Zn ions exposed at the surface. The most energetically favorable doped surface was decorated with (AgO)m nanoparticles of different sizes (1 ≤ m ≤ 6) which were sited at different relative positions to the Fe atom. The simulated work function explains the reactivity trends of the surface models, while the scanning tunneling microscopy images are in agreement with experimental data when the (AgO)m cluster is placed over the dopant. The interface formed between the substrate and the nanoparticle is essential to enable the ethanol conversion into ethanal, suggesting that dehydrogenation plays a key role in the alcohol detection.
0) surface to improve ethanol sensing. Using thermodynamic arguments, we have investigated the substitutional Fe doping of the symmetrically different Zn ions exposed at the surface. The most energetically favorable doped surface was decorated with (AgO)m nanoparticles of different sizes (1 ≤ m ≤ 6) which were sited at different relative positions to the Fe atom. The simulated work function explains the reactivity trends of the surface models, while the scanning tunneling microscopy images are in agreement with experimental data when the (AgO)m cluster is placed over the dopant. The interface formed between the substrate and the nanoparticle is essential to enable the ethanol conversion into ethanal, suggesting that dehydrogenation plays a key role in the alcohol detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...