Rapid activation of Co3O4 cocatalysts with oxygen vacancies on TiO2 photoanodes for efficient water splitting†
Abstract
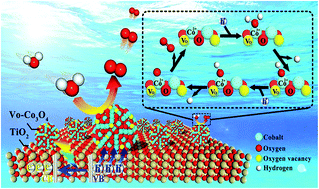
Cobalt oxide (Co3O4) has been extensively utilized as a promising oxygen evolution reaction (OER) cocatalyst for solar photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting. However, the relationship between its oxygen vacancies and PEC conversion efficiency has yet to be determined. Herein, we demonstrate a rapid and highly efficient strategy for rationally constructing oxygen vacancies on Co3O4 cocatalysts by Ar-plasma treatment, which could significantly enhance the PEC water oxidation reactivity of TiO2-based photoanodes. The photocurrent density could be achieved up to 2.5 mA cm−2 (1.23 VRHE) under AM 1.5G irradiation (100 mW cm−2), up to 2 times higher than that of the untreated Co3O4/TiO2 samples. More specifically, the oxygen vacancy formation on Co3O4 cocatalysts not only facilitates the hole trapping ability for promoting interfacial charge separation and migration, but also provides more active sites for water oxidation. The rapid and highly efficient activation of OER cocatalysts by producing oxygen vacancies may be potentially a universal strategy for improving the photo-conversion efficiency of PEC photoanodes now available.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...