Carbon-thin-layer protected WP with no passivation supported on acid-treated expanded graphite as efficient Pt Co-catalysts for methanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions†
Abstract
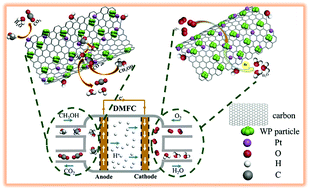
Application of direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs) is hampered by the low activity, poor stability, and low CO/methanol tolerance of Pt-based catalysts used for methanol oxidation reaction (MOR)/oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). In this study, tungsten phosphide-embedded carbon-thin-layer/acid-treated expanded graphite (WP-CL/AEG) composites are synthesized as Pt-supports/co-catalysts for MOR/ORR via a one-step synthesis route. For MOR, Pt-WP-CL/AEG-3 (molar ratio of P to AEG is 3.6 in precursor) shows the highest electrochemical surface area (123.05 m2 gPt−1) and mass activity (2217.6 mA mgPt−1), which are respectively 1.92 and 4.44 times higher than those of commercial Pt/C (64.16 m2 gPt−1 and 499.2 mA mgPt−1). Pt-WP-CL/AEG catalysts also exhibit higher CO tolerance and stability than Pt/C. Moreover, Pt-WP-CL/AEG-3 also exhibits a higher ORR activity than Pt/C in acidic media, mainly via a 4e− transfer pathway (OH− as the main product) for ORR. As expected, AEG greatly enhances the charge transfer capacity of Pt-WP-CL/AEG catalysts; the exposed P active sites induced by W atoms on WP facilitate methanol/O2 adsorption and activation during MOR/ORR; the CL originated from citric acid can protect WP from being oxidized in air, which contributes to high activity and stability of P active sites; and charges are transferred from AEG (positively charged) to WP via the linked-CL and then from WP to Pt, which contributes to the high MOR/ORR activity of Pt-WP-CL/AEG. It indicates that WP-CL/AEGs can be considered as promising supports/co-catalysts for Pt in MOR/ORR.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...