High-performance thermoelectric bracelet based on carbon nanotube ink printed directly onto a flexible cable†
Abstract
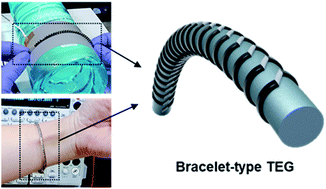
As future thermoelectric generators (TEGs) require flexibility and mass-producibility, the demand for high-performance TEGs based on printed thermoelectric (TE) materials is growing. Herein, we have rationally designed a bracelet-type TEG structure where the carbon nanotube (CNT) ink is printed in the in-plane direction of a flexible cable and the device is operated in the out-of-plane direction of the heat source. This is the first report to fabricate a flexible TEG by printing the TE ink on a curved surface. For printing the CNT ink on a curved surface, the viscosity, dispersibility, and TE performance of the CNT ink have been fundamentally studied. Especially, the mechanism of the solvent effect on the dispersion and viscosity of the CNT ink during planetary ball milling has been clarified. The flexible TEG based on 60 pairs of n- and p-doped CNT ink shows the maximum power output of 1.95 μW at a temperature difference of 30 K, which is one of the highest power outputs for flexible TEGs based on CNT inks. The ease of installment of the bracelet-type TEG on heat sources with various shapes and its ability to harvest waste heat in the out-of-plane direction of the heat source has great potential as flexible/or wearable power conversion devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...