Efficient polysulfide barrier of a graphene aerogel–carbon nanofibers–Ni network for high-energy-density lithium–sulfur batteries with ultrahigh sulfur content†
Abstract
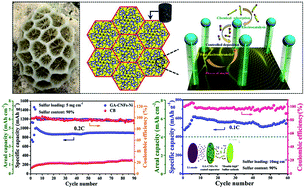
Low sulfur loading and content, as well as severe shuttle effects, remain the key issues for the application of lithium–sulfur (Li–S) batteries, resulting in a low areal capacity and fast capacity fade. Herein, a highly efficient conductive network is developed by growing herringbone structured carbon nanofibers (CNFs) on the surface of graphene aerogel (GA–CNFs–Ni) and is further applied as a functional coating layer in Li–S batteries. The conductive coating layer, serves as both a shield to trap the active materials detached from the cathode and a conductive “second current collector” to reactivate the trapped active materials. The herringbone structured CNFs enriched with defects and gaps enlarge the available reaction site for electrons, the electrolyte and sulfur species, ensuring the smooth operation of the sulfur cathode with high loading and high content. In addition, the uniformly distributed Ni nanoparticles also exert strong chemical bonding with polysulfides by first-principle calculations. Consequently, the GA–CNFs–Ni coated separator enables the “double high” sulfur cathode (5 mg cm−2, 90 wt%) to display an ultrastable cycle capability and superior rate performance. Moreover, a high sulfur loading of 10 mg cm−2 and a low electrolyte/sulfur (E/S) ratio (6 μL mg−1) are obtained, delivering a high areal capacity of 5.5 mA h cm−2 after 60 cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...