Sequential precipitation induced interdiffusion: a general strategy to synthesize microtubular materials for high performance lithium ion battery electrodes†
Abstract
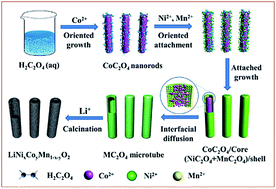
1D hollow structures are of great interest for wide applications, owing much to their kinetic transport advantages, but their facile synthesis through rational design remains a key challenge. In this work, we report for the first time a sequential precipitation induced interdiffusion strategy to synthesize a series of tubular electrode materials by the lithium impregnation and annealing of tube-like oxalate precursors. Different from conventional Ostwald ripening-induced mass migration within a single component, here the sequential precipitation is designed to promote non-equilibrium interdiffusion between different components, thus hollowing out the core. We show the wide scope of this strategy by rationally designing hollow electrode materials of multi-metal oxides. In particular, the syntheses of the most promising high energy cathode materials, Ni-rich LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 and Li-rich Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 microtubes, have been demonstrated, which deliver excellent electrochemical performance in terms of the initial coulombic efficiency, reversible capacity, rate capability and cycling stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...