Antisolvent processing of lead halide perovskite thin films studied by in situ X-ray diffraction†
Abstract
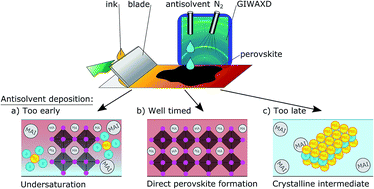
The conversion mechanism from the precursor ink to the perovskite film using antisolvent-induced crystallization has been studied using in situ X-ray diffraction during blade coating and antisolvent deposition. We study various solvent systems forming methylammonium lead iodide perovskite. We find that it is critical to add the antisolvent before the formation of a crystalline intermediate phase. Compared to thermal crystallization, the antisolvent-induced crystallization alters the conversion route. Instead of heterogeneous nucleation and conversion through a crystalline intermediate phase, antisolvent-assisted annealing leads to a rapid direct crystallization, resulting in highly regular smooth films.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...