Molecular simulation and experimental investigation of CO2 capture in a polymetallic cation-exchanged 13X zeolite
Abstract
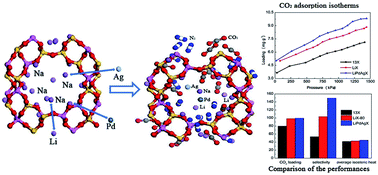
There is a great need to synthesize high-performance adsorbents for potential application in post-combustion CO2 capture. In this study, molecular simulation was employed to mimic cation exchanges in 13X zeolite with different amounts of Li+, K+, and Ca2+, providing guidance for the design of high-performance cation-exchanged zeolite. The separation performance of each cation-exchanged zeolite was evaluated in detail in terms of its pore volume, adsorption isotherm, energy, isosteric heat, and CO2/N2 selectivity. The simulated results showed that the fresh LiX-80 zeolite sample was the most promising adsorbent for CO2/N2 separation. On this basis, a novel polymetallic cation-exchanged zeolite was developed by introducing Pd2+ and Ag+ into LiX-80 (LiPdAgX). LiPdAgX exhibited a higher CO2 loading and higher CO2/N2 selectivity than 13X and LiX-80 zeolites. Finally, adsorption experiments were performed on the 13X, LiX, and LiPdAgX zeolites, and the order of the experimental results (13X < LiX < LiPdAgX) agrees well with the simulated order. This study provides microscopic-level insights into gas adsorption and separation in polymetallic cation-exchanged zeolites, and suggests that LiPdAgX zeolite can effectively enhance CO2 capture.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...