Experimental and theoretical investigation into visible-light-promoted selective hydrogenation of crotonaldehyde to crotonyl alcohol using Au–Co,Ni alloy nanoparticle supported layered double hydroxides†
Abstract
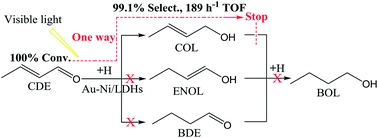
In this paper, Au–Co/Ni bimetal supported layered double hydroxides (Au–Co,Ni/LDHs) were synthesized for the hydrogenation reaction of crotonaldehyde (CDE) to crotonyl alcohol (COL) with both high conversion and selectivity under light irradiation. The hydrogenation experimental results indicated that both the hydrogenation conversion of CDE and the selectivity of COL have been greatly improved by Au–Co,Ni/LDHs under visible light irradiation, with the best turnover frequency performance of 189 h−1, 100% conversion and 99.1% selectivity (using Au–Ni/LDHs). Such high properties are attributed to a synergistic effect of localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of Au nanoparticles, and the additional Co or Ni species would further enhance this effect. The DFT calculation of CDE hydrogenation at Au–Co,Ni/LDHs showed that the hydrogenation happens at C2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O1 first to produce COL by following mechanism A2. Au–Ni/LDHs with lower activation energy had higher catalytic activity than Au–Co/LDHs. Further calculation showed that the COL hydration reaction can be hindered on Au–Co,Ni/LDHs compared to the unmodified Au/LDHs, which indicates that the introduction of second metal Ni or Co besides Au could further increase the COL productivity. The DFT calculations well explained and supported the experimental results.
O1 first to produce COL by following mechanism A2. Au–Ni/LDHs with lower activation energy had higher catalytic activity than Au–Co/LDHs. Further calculation showed that the COL hydration reaction can be hindered on Au–Co,Ni/LDHs compared to the unmodified Au/LDHs, which indicates that the introduction of second metal Ni or Co besides Au could further increase the COL productivity. The DFT calculations well explained and supported the experimental results.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...