Electrospun nanofiber substrates that enhance polar solvent separation from organic compounds in thin-film composites†
Abstract
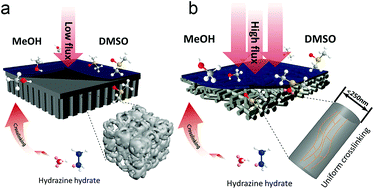
Organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN) with thin film composite (TFC) membranes containing a thin selective layer on top of a porous substrate is key to lowering the energy costs of high-speed chemical separations. Conventional TFC membranes were often built on phase inversion induced asymmetrical substrates with high tortuosity that impedes rapid solvent transport. Nanofibers as ultrapermeable substrates have enhanced water transport in forward osmosis, nanofiltration and other aqueous separations. However, problems of solvent stability under harsh operating conditions prevent their exploitation in non-aqueous molecular separations. Here we show that by combining a simple solution-phase cross-linking process and electrospinning, the instability of nanofibrous polyacrylonitrile (PAN) in industrially important polar solvents can be overcome and harnessed to benefit the purification of polar solvents containing low molecular weight solutes. The low tortuosity of electrospun PAN nanofibrous substrates is key to uniform cross-linking, and hence they are more stable and mechanically stronger than cross-linked PAN asymmetrical substrates fabricated by the traditional approach of phase inversion. The low resistance offered by cross-linked nanofibrous substrates increased solvent permeation without sacrificing selectivity, for example, to 99.5% rejection of negatively charged Sudan 4 (MW: 380 Da) dye with a methanol permeance of 9.87 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 and water permeance of 22.40 L m−2 h−1 bar−1. The enhanced stability of TFC membranes in polar aprotic solvents such as dimethylsulfoxide highlights their potential application for molecular separations in pharmaceutical and chemical industries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...