Azetidinium lead iodide: synthesis, structural and physico-chemical characterization†
Abstract
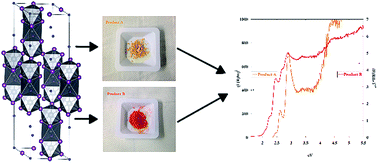
The synthesis of an azetidinium lead iodide perovskite (CH2)3NH2PbI3 (AzPbI3), and its extensive characterization are reported. The compound was synthesized through a simple approach based on the reaction between an azetidine aqueous solution and lead acetate dissolved in an excess of hot concentrated aqueous HI. The compound was recrystallized by the vapor diffusion method. Since the synthesized AzPbI3 crystals consistently turned out to be twinned and disordered, the structure determination was performed by using powder X-ray diffraction data analysis procedures. The material was found to possess a quite complex and large rhombohedral crystal structure with a zig-zag array of groups composed of three PbI6 octahedra sharing faces along the c-axis. Unfortunately, because of the extended cationic sublattice disorder and of the large X-ray scattering factor difference between the atoms composing the (CH2)3NH2PbI3 (AzPbI3) unit cell, the position of azetidinium cations could not be determined with confidence. The material was also characterized by CHN, ESI-MS analyses and FT-IR spectroscopy in order to verify its chemical composition. Furthermore, TG-DTA coupled to quadrupole mass spectrometry, temperature-controlled powder XRD and Knudsen effusion mass spectrometry were employed to evaluate the thermal stability of the material. Besides, diffuse reflectance UV-vis spectroscopy and PL measurements were carried out to investigate the optical properties of the material. Optical properties turned out to be very sensitive to preparative conditions. In addition, a test of mutual solid solubility with methylammonium lead iodide, CH3NH3PbI3, was performed by co-precipitation of both perovskites. Powder XRD clearly showed mutual solubility. Hence, the higher basicity of azetidine compared to that of methylamine may enhance the stability of solid solutions made out of the two perovskites with respect to the hydrolysis of pure CH3NH3PbI3 thus increasing the lifetime of perovskite solar devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...