In situ synthesis of hierarchical MoSe2–CoSe2 nanotubes as an efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction in both acidic and alkaline media†
Abstract
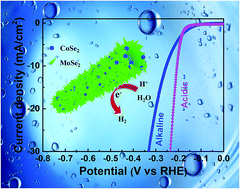
Hierarchical MoSe2–CoSe2 nanotubes (MS–CS NTs) are in situ converted from the CoMoO4 nanowires (NWs) via a facile hydrothermal selenization method. As an electrocatalyst, MS–CS NTs show highly efficient and stable performance for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). In acidic (or alkaline) medium, MS–CS NTs demonstrate superior HER performance with a very low onset overpotential of 148 (or 127) mV vs. RHE, a low overpotential of 206 (or 237) mV vs. RHE at −10 mA cm−2, a very large current density of 84.6 (or 23.5) mA cm−2 at −300 mV (vs. RHE), a small Tafel slope of 45 (or 89) mV dec−1 and remarkable long-term cycling stability. The outstanding HER activity of MS–CS NTs in both media is attributed to their unique hierarchical and nanoporous architecture constructed with the homogeneous distribution of few-layered MoSe2 nanosheets and CoSe2 nanoparticles, which can not only efficaciously suppress the aggregation of MoSe2 nanosheets, but also generate more active sites or edges to take part in the HER. In addition, the uniform dispersion of highly conductive CoSe2 nanoparticles in few-layered MoSe2 nanosheets efficiently promotes the electron transfer from the electrode to the active sites on MoSe2 nanosheets, further improving the electrocatalytic properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...