Aqueous rechargeable dual-ion battery based on fluoride ion and sodium ion electrochemistry†
Abstract
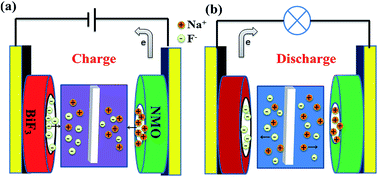
The anion battery system is a new research area in the energy storage field. Herein, a novel aqueous rechargeable dual-ion battery based on fluorine ion and sodium ion electrochemistry is proposed, consisting of bismuth fluoride as the anode, sodium manganese oxides (NMO) as the cathode and aqueous NaF solution as the electrolyte. The bismuth fluoride electrode can electrochemically release/capture fluoride ion in aqueous electrolyte and sodium ion can be de-intercalated/intercalated at the NMO cathode during charge/discharge process. The electrochemical behavior was confirmed by cyclic voltammetry, charge–discharge curves as well as X-ray powder diffraction. The reversible and stable discharge capacity is obtained with a coulombic efficiency of 98.44%. After 40 cycles, the specific capacity can be still maintained at 47.28 mAh g−1 at the current density of 100 mA g−1. The current battery system possesses excellent rate performance. It can operate at 3200 mA g−1 (10.6C) with 82.8% specific capacity as that at 100 mA g−1. This is the first demonstration that the aqueous dual-ion battery can work based on fluoride ion and sodium ion electrochemistry and it will be significant for future energy storage and ion removal.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...