Enhanced redox activity of a hollow conjugated microporous polymer through the generation of carbonyl groups by carbonylative Sonogashira coupling†
Abstract
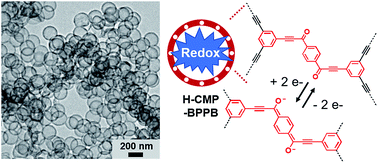
Redox active 1,4-bis(3-phenylpropynoyl)benzene moieties were incorporated into a hollow conjugated microporous polymer via carbonylative Sonogashira coupling of 1,3,5-triethynylbenzene with 1,4-diiodobenzene in the presence of carbon monoxide. The resultant redox active material showed enhanced energy storage performance for pseudocapacitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...