Electrospun membranes of imidazole-grafted PVDF-HFP polymeric ionic liquids for highly efficient quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
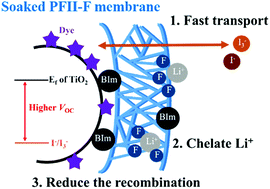
Three novel polymeric ionic liquids (PILs), denoted as PFII-F, PFII-E, and PFII-S, are successfully synthesized by grafting different molar ratios (one-fourth, one eighth, and one sixteenth, respectively) of 1-butylimidazolium iodide onto poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP). These PFII PILs are fabricated as polymer membranes via a simple electrospinning technique, which are used as the electrolyte for quasi-solid-state (QSS) dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). The PFII membranes have multiple functions including: (1) encapsulation of the liquid electrolyte with good charge transfer and ionic conductivity properties, (2) chelation of Li+ through the lone pair electrons on their fluoride atoms, and (3) filling the dye-uncovered TiO2 surface with their imidazolium segment. Function (1) endows DSSCs with prominent long-term stability, while functions (2) and (3) suppress the dark current. The best QSS-DSSC with the PFII-F membrane shows a larger open-circuit voltage (VOC), comparable short-circuit current density (JSC), better power conversion efficiency (η) of 9.26%, and superior long-term stability (up to 97% of its initial η) over 1500 h compared to the cell with standard liquid electrolyte (8.63%).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...