Novel safer phosphonate-based gel polymer electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries with excellent cycling performance†
Abstract
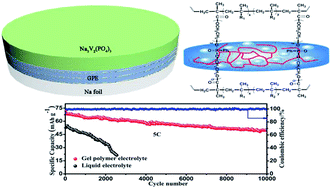
Gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs) are one of the most promising candidates to solve safety issues such as liquid leaking, fire, and explosions in battery systems. In this work, novel phosphonate-based porous cross-linked gel polymer electrolytes were synthesized by in situ thermal polymerization and applied to sodium-ion batteries. The phosphorus containing GPEs have a high ionic conductivity of 6.29 × 10−3 S cm−1 and an excellent electrochemical stability of up to 4.9 V (vs. Na+/Na), and thus could be used as possible non-flammable electrolytes. The Na3V2(PO4)3/GPE/Na cell using GPEs and a Na3V2(PO4)3 cathode yields a high capacity of 110.7 mA h g−1 at 1C rate. Moreover, an excellent long-term cycling stability at 5C rate was observed, retaining 81.8% and 69.2% capacity after long-term 4500 and 10 000 cycles, respectively. When cycled at high temperature (60 °C), the sodium-ion Na3V2(PO4)3 cell with the GPE also exhibits superior cycling stability compared to a battery with a conventional liquid electrolyte. The excellent cycling performances of the SnS2/GPE cell and full cell of SnS2/NVP were also observed, holding great promise for the production of safer phosphonate-containing battery systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...