Solution-processable flexible thermoelectric composite films based on conductive polymer/SnSe0.8S0.2 nanosheets/carbon nanotubes for wearable electronic applications†
Abstract
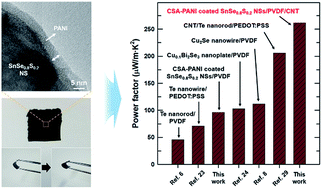
Flexible thermoelectric composite films consisting of conductive polyaniline (PANI)-coated SnSe0.8S0.2 nanosheets (NSs) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are fabricated via a solution processing procedure. The SnSe0.8S0.2 NSs are chemically exfoliated from a bulk ingot, and camphorsulfonic acid-doped PANI (CSA-PANI) is coated on the surface of the SnSe0.8S0.2 NSs. The thermoelectric properties of the composite film can be further enhanced by introducing a small amount of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) into the composite. The maximum thermoelectric power factor of the CSA-PANI-coated SnSe0.8S0.2 NS/PVDF/CNT composite film is 297 μW m−1 K−2 at 400 K, which is significantly higher than that of the CSA-PANI-coated SnSe0.8S0.2 NS/PVDF composite film without CNTs. The incorporation of SnSe0.8S0.2 NSs and conductive PANI mixed with CNTs is a promising strategy to realize high-performance flexible thermoelectric applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...