Stability of polymeric separators in lithium metal batteries in a low voltage environment
Abstract
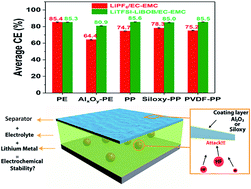
The separator is an important component in rechargeable lithium (Li) metal batteries; however, less attention has been focused on it so far. In this work, several representative separators based on polyolefins without and with ceramic and polymeric coatings were selected to study the stability of separators against Li metal anode in Li‖Cu and Li‖Li coin cells in a low voltage environment less than 1 V vs. Li/Li+. Moreover, two representative electrolytes of LiPF6 and LiTFSI–LiBOB in a carbonate solvent mixture were also employed to systematically study their interactions with separators in Li metal cells. It was found that separators could largely affect the coulombic efficiency and cycling stability of Li metal cells, especially when using the LiPF6 electrolyte, which is probably due to the effect of the trace amount of HF in the LiPF6 electrolyte. Among these separators, polyethylene separator is the most stable one with Li metal while ceramic and polysiloxy coating layers are not stable with Li metal in the presence of the LiPF6 electrolyte. This work gave more insights into the above phenomena, which could provide references for Li metal battery studies when employing Li‖Cu and Li‖Li cells in a low voltage environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...