Electrochemical and electrocatalytic reaction characteristics of boron-incorporated graphene via a simple spin-on dopant process†
Abstract
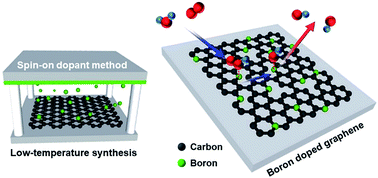
Chemical doping is one of the most effective methods to tune the electrochemical properties of graphene. We report a simple and relatively low-temperature process for the fabrication of boron doped graphene by using a spin-on dopant (SOD) method. SOD-treated graphene was successfully doped with boron atoms at a temperature lower than 600 °C. The fabricated boron doped graphene exhibits a specific capacitance of 4 mF cm−2, as well as a high-rate performance of 91.9% at 200 mV s−1 as an electrode material for pseudocapacitors. It also shows excellent oxygen reduction activity and durability with a current retention of 91.4% and methanol-tolerance properties. These features are beneficial for catalyst applications in the oxygen reduction reaction due to well-engineered boron sites with high electrical conductivity and many active sites for electrochemical reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...