Metal organic framework based mixed matrix membranes: an overview on filler/polymer interfaces
Abstract
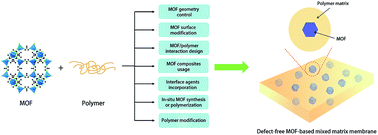
Membrane technology for gas separation has attracted significant attention because of its low energy consumption. However, most polymeric membranes suffer from the trade-off between mass transport rates and separation efficiency. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising candidates to fabricate mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) for gas separation due to their high surface area and porosity, adjustable pore sizes and controllable surface functionality. This review presents the recent opportunities and challenges faced in MOF-based MMM fabrication, emphasizing the MOFs/polymer interfacial morphology. The state-of-the-art solutions and strategies for improving the filler/matrix interface are reviewed and evaluated in detail. Finally, the characterisation and understanding of the MMM interface morphology and future research directions are outlined. This review will offer some insights for fabricating MMMs with optimal interface morphology and separation performance.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...