The effect of particle wettability on the stick-slip motion of the contact line
Abstract
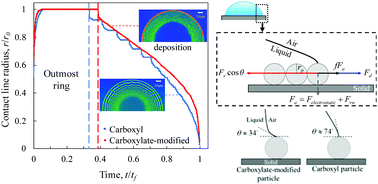
Contact line dynamics is crucial in determining the deposition patterns of evaporating colloidal droplets. Using high-speed interferometry, we directly observe the stick-slip motion of the contact line in situ and are able to resolve the instantaneous shape of the inkjet-printed, evaporating pico-liter drops containing nanoparticles of varying wettability. Integrated with post-mortem optical profilometry of the deposition patterns, the instantaneous particle volume fraction and hence the particle deposition rate can be determined. The results show that the stick-slip motion of the contact line is a strong function of the particle wettability. While the stick-slip motion is observed for nanoparticles that are less hydrophilic (i.e., particle contact angle θ ≈ 74° at the water–air interface), which results in a multiring deposition, a continuous receding of the contact line is observed for more hydrophilic nanoparticles (i.e., θ ≈ 34°), which leaves a single-ring pattern. A model is developed to predict the number of particles required to pin the contact line based on the force balance of the hydrodynamic drag, interparticle interactions, and surface tension acting on the particles near the contact line with varying particle wettability. A three-fold increase in the number of particles required for pinning is predicted when the particle wettability increases from the wetting angle of θ ≈ 74° to θ ≈ 34°. This finding explains why particles with greater wettability form a single-ring pattern and those with lower wettability form a multi-ring pattern. In addition, the particle deposition rate is found to depend on the particle wettability and vary with time.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...