Rheology and microstructure of concentrated microcrystalline cellulose (MCC)/1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (AmimCl)/water mixtures†
Abstract
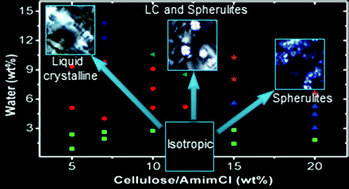
Water added to a solution of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) in 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (AmimCl) reduces the solvent quality and causes significant changes in the flow properties and microstructure due to restructuring and aggregation of cellulose molecules. We report an experimental investigation by means of polarization optical microscopy (POM) and rheology of the distinct phases formed in 5–20 wt% MCC/AmimCl solutions due to the addition of water. With increase in the cellulose concentration, the MCC/AmimCl/water mixtures showed different morphologies such as the non-aligned cholesteric liquid crystalline (LC) domain, the coexistence of spherulite-like structures within the LC domain and a space-spanning network of spherulite-like structures at high concentrations of water. In situ microscopy during shear and POM observations pre and post shear revealed a significant increase in the size of the birefringent domains as the shear rate is increased, which continued to exist even after the cessation of shear. With an increase in the concentration of water, the zero shear viscosity of the MCC/AmimCl/water mixtures was found to go through a minimum, beyond which the aggregation of cellulose commenced. The corresponding oscillatory shear response showed a sol–gel transition with an increase in water concentration. Moreover, at high cellulose concentrations (12–20 wt%), the MCC/AmimCl/water gels exhibited self-similarity and followed the Chambon-Winter (CW) criterion. The similar phase behavior and rheological response observed for MCC dissolved in 1-butyl-3 methylimidazolium chloride (BmimCl) indicated the generality of the presented results.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...