Active cargo transport with Janus colloidal shuttles using electric and magnetic fields†
Abstract
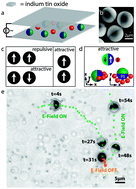
Active colloids show non-equilibrium behavior that departs from classical Brownian motion, thus providing a platform for novel fundamental phenomena and for enticing possible applications ranging from water treatment to medicine and microrobotics. Although the physics, motion mechanisms and guidance have been extensively investigated, active colloids are rarely exploited to simultaneously guide and transport micron-sized objects in a controllable and reversible manner. Here, we use autonomous active Janus particles as colloidal shuttles to controllably transport cargo at the microscale using external electric and magnetic fields. The active motion arises from the metallodielectric characteristics of the Janus particles, which allows them to also trap, transport and release cargo particles through dielectrophoretic interactions induced by an AC electric field. The ferromagnetic nature of the nickel layer that forms the metallic hemisphere of the Janus colloids provides an additional mechanism to direct the motion of the shuttle using an external magnetic field. With this highly programmable colloidal system, we are able to harness active colloid motion and use it to transport cargo particles to specific destinations through a pre-defined route. A simple analytical model is derived to successfully describe the motion of the shuttle–cargo assembly in response to the applied electrical field. The high level of control on cargo pick-up, transport and release leads to a powerful delivery tool, which could eventually be used in microactuators, microfluidics or for controlled delivery within organ-on-a-chip devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...