Engineered interaction between short elastin-like peptides and perfluorinated sulfonic-acid ionomer†
Abstract
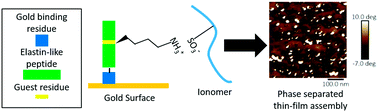
Control of ionomer thin films on metal surfaces is important for a range of electrodes used in electrochemical applications. Engineered peptides have emerged as powerful tools in electrode assembly because binding sites and peptide structures can be modulated by changing the amino acid sequence. However, no studies have been conducted showing peptides can be engineered to interact with ionomers and metals simultaneously. In this study, we design a single-repeat elastin-like peptide to bind to gold using a cysteine residue, and bind to a perfluorinated sulfonic-acid ionomer called Nafion® using a lysine guest residue. Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring and atomic force microscopy are used to show that an elastin-like peptide monolayer attached to gold facilitates the formation of a thin, phase-separated ionomer layer. Dynamic light scattering confirms that the interaction between the peptide with the lysine residue and the ionomer also happens in solution, and circular dichroism shows that the peptides maintain their secondary structures in the presence of ionomer. These results demonstrate that elastin-like peptides are promising tools for ionomer control in electrode engineering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...