Polyelectrolyte complex films influence the formation of polycrystalline micro-structures†
Abstract
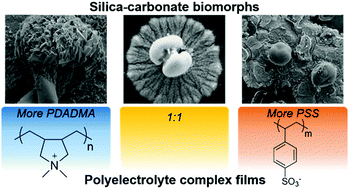
Silica–carbonate biomorphs are inorganic materials composed of thousands of crystalline nanorods that assemble complex morphologies such as helices, vessels, and sheets. We investigate the effect on biomorph crystallization of polyelectrolyte complex films that are prepared using the layer-by-layer deposition technique and post-processed to obtain three stable, chemically distinct films. Biomorph growth on poly(diallyldimethylammonium)-dominated substrates (cationic) shows polycrystalline helical and sheet structures bounded by large witherite prisms. Crystallization on poly(styrenesulfonate)-dominated (anionic) and stoichiometric substrates follows a qualitatively different pathway. We observe islands of radial mineral films that over several days extend at a remarkably constant velocity of 0.48 μm h−1 and eventually mineralize the whole substrate. Our work opens exciting avenues for the use of polyelectrolyte films as tunable substrates for biomimetic crystallization.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...