Design of cyclopentadithiophene-based small organic molecules as hole selective layers for perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
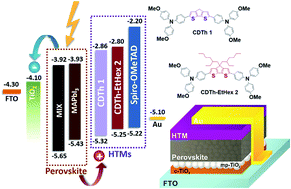
Thiophene-based p-type molecules are being extensively investigated and employed in optoelectronic devices due to their intriguing semiconducting properties. Herein, we report the synthesis and characterization of a 4H-cyclopenta[1,2-b:5,4-b′]dithiophene-based core, having methoxy-substituted triphenylamine side arms as donor groups. These rationally designed molecules were obtained through easy cross-coupling reactions, in few synthetic and purification steps. The synthesized molecules coded as CDTh 1 and CDTh-EtHex 2 showed excellent thermal stability, and the fabricated perovskite solar cells using CDTh 1 and CDTh-EtHex 2 as hole transporting materials (HTMs) gave competitive performance compared to the state-of-the-art Spiro-OMeTAD. Photoluminescence of perovskite layers coated with these HTMs show relatively high quenching suggesting the injection of holes from the valence band of the perovskite into the HOMO of the HTM. The estimated production cost was calculated and found to be a fraction of that of commercially available state-of-the-art Spiro-OMeTAD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...