Abstract
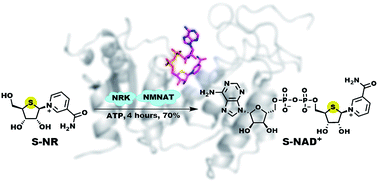
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an essential cofactor participating in a variety of important enzyme-catalyzed physiological and pathophysiological processes. Analogues of NAD+ provide key and valuable agents for investigating NAD+-dependent enzymes. In this study, we report the preparation of a novel stable NAD+ mimic, 4′-thioribose NAD+ (S-NAD+), using a facile and efficient chemoenzymatic approach. Substrate activity assays indicated the resulting S-NAD+ is chemically inert to human CD38 and sirtuin 2 enzymes, but capable of participating in redox reactions in a manner similar to NAD+. X-ray crystallographic analysis revealed binding of S-NAD+ to the active site of human CD38 and critical residues involved in leaving group activation and catalysis. By more closely mimicking NAD+ in geometry and electrostatics, the generated S-NAD+ offers a unique and important tool that can be extended to study enzymes utilizing NAD+.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...