Fluorogenic thiazole orange TOTFO probes stabilise parallel DNA triplexes at pH 7 and above†
Abstract
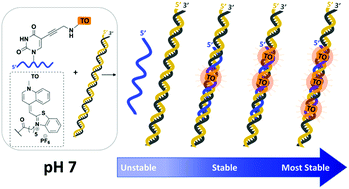
The instability of DNA triplexes particularly at neutral pH and above severely limits their applications. Here, we demonstrate that the introduction of a thiazole orange (TO) intercalator onto a thymine nucleobase in triplex forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) resolves this problem. The stabilising effects are additive; multiple TO units produce nanomolar duplex binding and triplex stability can surpass that of the underlying duplex. In one example, a TFO containing three TO units increased the triplex melting temperature at pH 7 by a remarkable 50 °C relative to the unmodified triplex. Notably, TO intercalation promotes TFO binding to target sequences other than pure polypurine tracts by the use of 5-(1-propynyl)cytosine (pC) against C:G inversions. By overcoming the instability of triplexes across a broad range of pH and sequence contexts, these very simple ‘TOTFO’ probes could expand triplex applications into many areas including diagnostics and cell imaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...