Carbohydrate-conjugated 4-(1,3,2-dithiarsolan-2-yl)aniline as a cytotoxic agent against colorectal cancer
Abstract
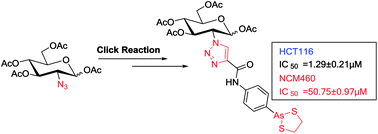
Arsenic trioxide (As2O3) has been approved for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL); however, its use in the treatment of solid tumors is limited due to its pharmacokinetic properties. Organic arsenic compounds provide better options for pharmaceutical optimization. p-Aminophenyl arsenoxide (p-APAO), an organic arsenic compound, was found to interact with the promyelocytic leukemia–retinoic acid receptor alpha (PML–RARα) fusion protein in a similar manner to arsenic trioxide. Analogs of p-APAO such as 4-(1,3,2-dithiarsolan-2-yl)aniline (p-APDTAs) were recently found to show improved cytotoxicity toward several solid tumor cell lines with lower toxicity to normal cells. Here, we synthesized a carbohydrate-conjugated 4-(1,3,2-dithiarsolan-2-yl)aniline (p-APDTAs) and showed that it exhibited reduced cytotoxicity to normal cells, suggesting a feasible approach to improve the therapeutic index of arsenic-containing compounds as chemotherapeutic agents.
- This article is part of the themed collection: A Decade of Progress in Click Reactions Based on CuAAC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...